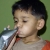
Helicobacter pylori infection is the most common bacterial infection in humans and its prevalence is much higher in low-and middle-income countries (around 80-90% among adults) than in high income countries (<40%). H. pylori infection can not only impact nutrient uptake and utilisation, but also increase the risk of gastritis, peptic ulcers and stomach cancer.
Helicobacter pylori infection
The 13C-Urea Breath Test (13C-UBT) is a well-established non-invasive stable isotope technique to diagnose the presence of H. pylori in the stomach for both diagnostic and research purposes.
Information on H. pylori infection can guide programme planners when designing supplementation and food fortification interventions to address anaemia among children and women of reproductive age.