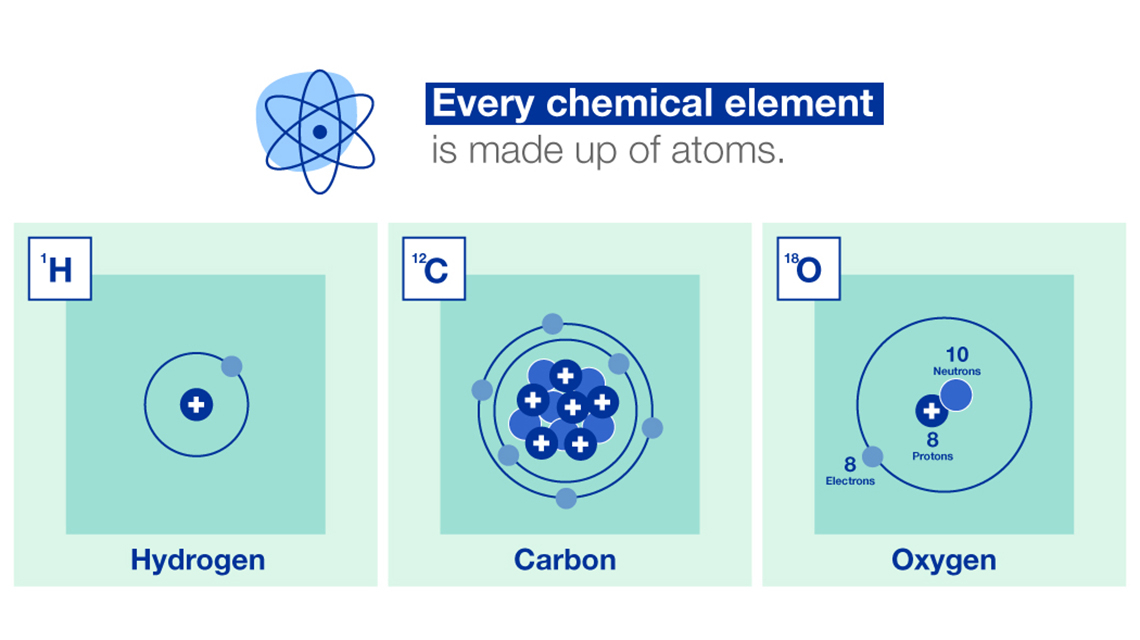
Nuclear and isotopic techniques can help us to better understand the world we live in. The data we gather with these techniques can lead to improved, science-based policy making, including in relation to climate change. We can study both land and water systems using various nuclear techniques to evaluate the effects of climate change on the environment.
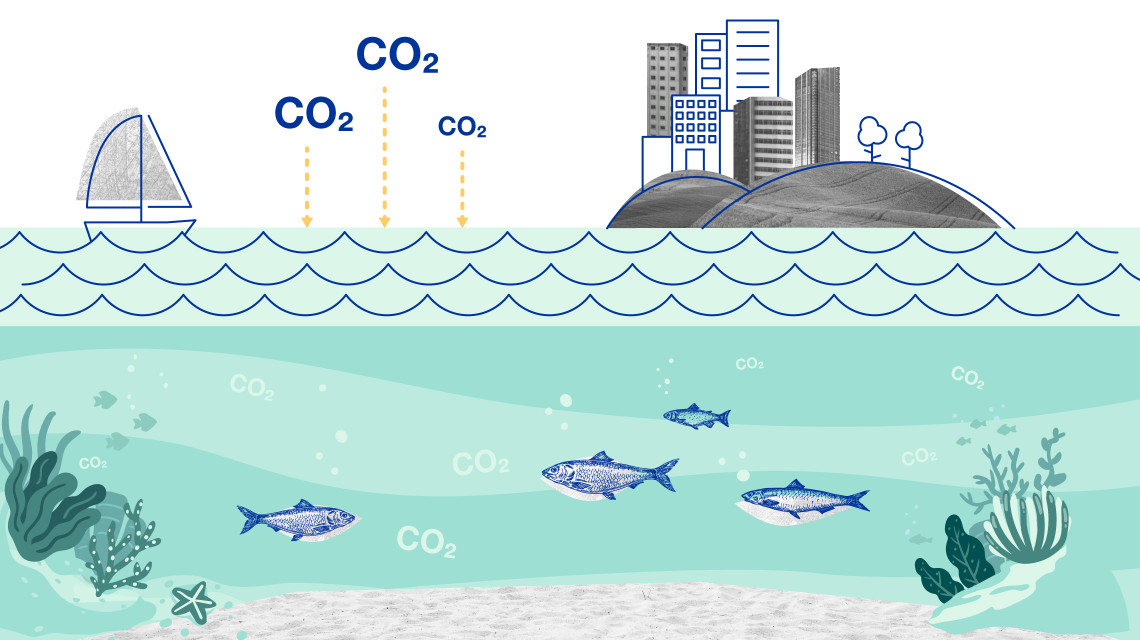
These techniques and tools are effective in monitoring greenhouse gas emissions such as carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrous oxide (N2O) and methane (CH4), understanding environmental changes to oceans, mountains and their ecosystems, and developing ways to adapt to food and water shortages exacerbated by changing weather patterns.
“Countries all over the world are increasingly recognising the value of using nuclear techniques to combat various challenges faced by climate change. They are discovering first-hand how beneficial the technologies promoted by the IAEA are,” said Najat Mokhtar, IAEA Deputy Director General and Head of the Department of Nuclear Sciences and Applications.
Data for identifying, monitoring and managing sources of greenhouse gas emissions are collected using isotopic techniques to understand how they are connected to changes occurring on land, in oceans and throughout the atmosphere. We explain how.